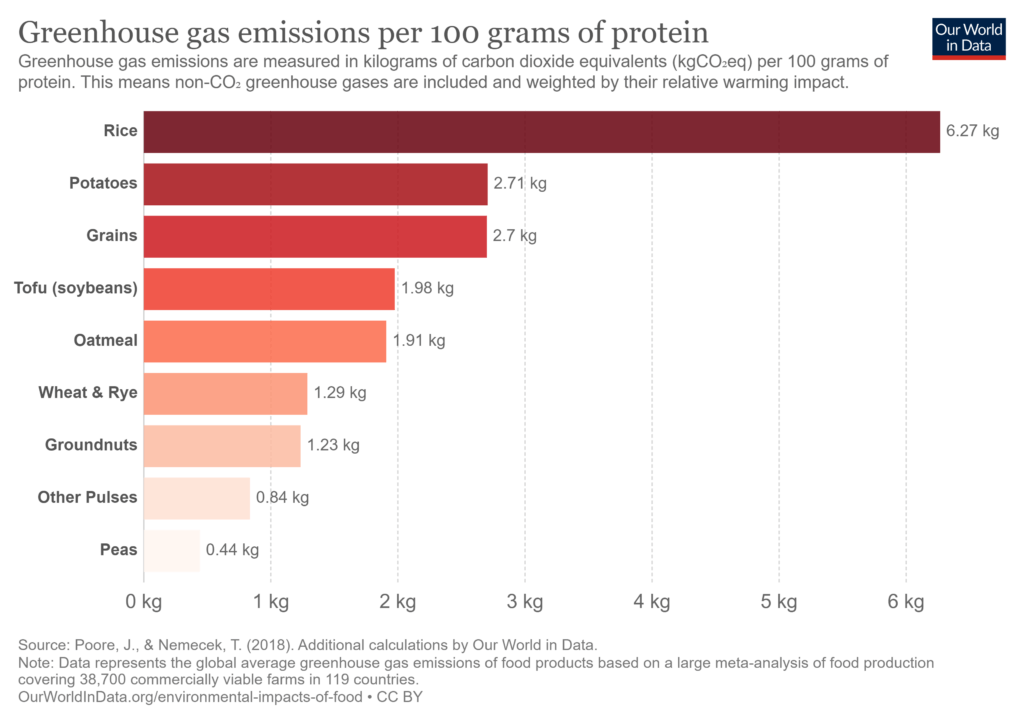Sourcing Best Plant Protein Based on Application Needs
Taste, Function and Sustainability Are Key Factors In Plant-Based Foods

For the past three years, plant-based foods have experienced an unprecedented surge in popularity. In 2022, the consumer demand for plant-based foods remained strong despite the rising inflation affecting the entire food industry. The plant-based market's massive growth prompted an increased demand for plant protein sources used to develop plant-based products.
It is no surprise that plant-based foods are gaining momentum on the food market as a mounting number of consumers discover the nutritional, environmental, and functional benefits plant-based foods provide. The main factors fueling the popularity of plant-based foods include a heightened consumer interest in health and wellness, proactive and holistic health management through improved nutrition, food sustainability, and ethical sourcing concerns.
In 2022, US plant-based food sales reached an impressive $8 billion, according to the SPINS report from Plant-Based Foods Association. What started as a vegan and vegetarian trend has inevitably penetrated other consumer categories. Today we can find plant-based foods on the plates of vegans, flexitarians, and omnivores alike.
The explosion of interest in plant-based eating opens viable opportunities for food manufacturers to launch new products and innovate with functional ingredients. However, it also has challenged food formulators to choose and source the best plant protein ingredients right for the "job" and meet the broad consumer demands. Diversifying protein sources and formulating with allergen-free proteins is important for the continued category growth.
CONSUMERS PERSPECTIVE ON PLANT-BASED FOODS
According to recent research, 80 percent of North American consumers read the ingredient lists and carefully study food labels and other claims on the packaging. Consumers are looking for sustainably sourced, non-GMO foods made with plant proteins that provide higher nutritional benefits while delivering excellent taste and organoleptic characteristics.
The top four reasons shoppers seek plant-based foods are Taste (52%), Health (39%), Environmental Impact (13%, and Animal Welfare (11%). According to the Food Allergy Research & Education data, one in four consumers are also looking for allergen-free products since 85 million people in America are trying to avoid consuming products that contain one of the top nine allergens. The right choice of the plant protein source that meets these criteria can be the key to formulation success. Paired with transparent labeling and a creative marketing message, it will certainly guarantee market success for a new plant-based product.
KEY PLAYERS AND NEWCOMERS IN PLANT PROTEIN SPACE
According to Giract, plant-based proteins enjoy a 70 percent of protein ingredient market share, making them the dominant source of protein used in food and feed. Soy and wheat are two of the most used protein sources worldwide. Soy was one of the first plant proteins that lead the plant-based food revolution a few years ago. In the past few years, soy and wheat comprised the bulk of the plant-protein-based food and drink products launched. But, in recent years, plant-based market pioneers have released innovative products based on pea, hemp, oat and rice, chickpea, and other plant protein newcomers. The popularity of pea-based protein has been growing quickly due to its high protein content, non-allergen status, non-GMO, and sustainability benefits.
IMPORTANT FACTORS TO CONSIDER WHEN CHOOSING PLANT PROTEINS
When food formulators choose the plant protein source, the key factors to consider are organoleptic properties, functionality, nutritional benefits, and environmental impact from production. Companies also consider cost in use of the chosen ingredient, supply reliability, and safety and quality protocols of the ingredient manufacturer.
If food formulators want to achieve lasting success with plant-based foods, they need to integrate a clean, hypoallergenic, and functional plant protein source within the product. While products like tofu and tempeh are excellent sources of protein and calcium, they are soy-based products that may deter both health-conscious consumers and those with a soy allergy. Wheat is a popular option for adding plant-based protein to formulations because its easily accessible and economical, but wheat-based products are not suitable for gluten-sensitive consumers. Another angle to consider is plant protein sustainability ranking. While soy and wheat are popular and readily available, they are less attractive in terms of their carbon footprint compared to other available plant-based protein sources.
Source: Our World in Data
WHY PEA PROTEINS ARE THE NEXT "BIG THING" FOR PLANT-BASED FOODS
Pea proteins have great potential in the plant-protein world. Pea proteins have been successfully used in various applications that can be found on the market shelves today, including plant-based milks, yogurt, snack bars, vegan meats, veggie burgers, and protein powders. Pea proteins can provide both technical and nutritional benefits and can be used in a wide variety of applications making them a highly versatile source of protein.
Pea protein comes from yellow peas (Pisum sativum L.), which belong to the pulse family. Compared to the other popular plant-protein sources, peas have low allergenicity and are non-GMO, making them a great alternative to soy and wheat products. Peas have a unique and clean taste, which allows for high incorporation in product formulations. Pea protein is available with a wide range of functionalities and offers food formulators the necessary technical benefits suitable for formulating plant-based meats, plant-based dairy alternatives, spreads, and more.
PEA PROTEIN ISOLATE DELIVERS A HIGHER PROTEIN CONTENT FOR BETTER NUTRITION
One of the main benefits of pea protein isolate is its high protein content and high digestibility. With an Amino Acid Score (AAS) of 0.96 and a digestibility rating of 98 percent, pea protein isolate is considered one of the best quality plant proteins. It can be used in food formulations to increase protein content in meat analogs, dairy alternatives, bakery, baked goods, and protein bars. Pea protein isolate is also rich in Lysine and Arginine.
Pea proteins have low antinutritional factors and are hypoallergenic, making them one of the most tolerated plant protein sources. Pea proteins can help restore the nutritional profile of plant-based products.
Nutritional superiority can also be achieved by blending pea protein with other plant-based proteins, like rice protein. Food formulators have been able to achieve a higher PDCAAS score of their plant-based products by combining different types of plant proteins to complete a full amino acid profile that makes a "complete protein." A higher PDCAAS value means the product delivers a higher percentage of the daily value (%DV) of protein to the human body, making it possible for food manufacturers to make attractive marketing claims on their plant-based products.
PEA PROTEIN ISOLATE OFFERS IMPROVED FUNCTIONAL BENEFITS
Food manufacturers working with pea protein isolate offered by A&B Ingredients value several advantages, including high solubility, clean taste, and an excellent mouthfeel.
Technical benefits, such as building texture or emulsification of oils and fats, are crucial attributes in food formulations and can be achieved with the right selection of pea proteins. A&B Ingredients offers a line of pea protein isolates that have been designed with functionality for specific applications. For example, specific Pisane™ pea protein isolates are available for baked goods applications, where reduced water absorption is critical for improved dough handling and processing.
In non-dairy beverages and creamer applications, food formulators choose pea protein isolate for their excellent emulsification properties to prevent oil and fat separation. Select Pisane™ pea protein isolates have excellent solubility, which can improve viscosity and mouthfeel in beverage applications.
PLANT PROTEIN WITH A LOWER ENVIRONMENTAL FOOTPRINT
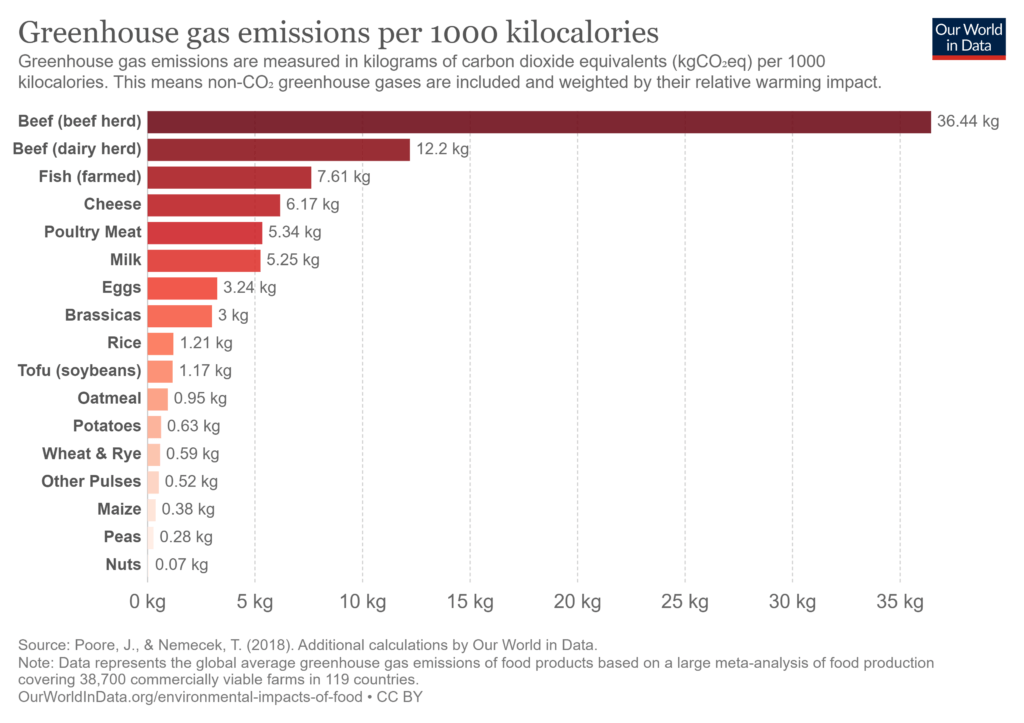
Pea protein causes limited greenhouse gas emissions, compared to other plant protein sources, and far less than animal protein, making it an attractive protein source from a sustainability standpoint. Less water is used during pea protein production compared to other protein sources, including soy and wheat.
Source: Our World in Data
Today's consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the importance of balanced nutrition and incorporating more plant-based options into their diet. Concerns regarding sustainability and climate change are prevalent in today's news. As people continue to learn about the effects of climate change, the astronomical water and energy demands in animal protein production, and its detrimental impact on the environment, consumers are more likely to purchase and eat plant-based proteins and foods. Ultimately, with the "right" plant protein and the "right" functionality, businesses can formulate and offer great-tasting plant-based substitutes to meet the needs of modern consumers.
How Can We Help?
We are here to help you with development of new and improved food products. Our technical service and sales teams can assist you in choosing the right ingredients best suited for your applications.
Product CatalogContact Us